BERT vs GPT: Writing Use Cases Compared

BERT and GPT are two powerful AI models designed for different writing tasks. BERT, developed by Google, focuses on understanding and analyzing text, making it ideal for editing, grammar checks, and sentiment analysis. GPT, created by OpenAI, excels at generating content, such as drafting articles, brainstorming ideas, and storytelling.
Key Points:
- BERT: Reads text bidirectionally, perfect for refining and analyzing content.
- GPT: Writes text sequentially, ideal for generating and expanding ideas.
- Use Case: BERT is best for precise editing; GPT is better for creating fluent, long-form content.
- Combining both models can enhance accuracy and creativity in writing.
Quick Comparison:
| Feature | BERT | GPT |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture Type | Encoder-only Transformer | Decoder-only Transformer |
| Directionality | Bidirectional (reads both ways) | Unidirectional (left to right) |
| Primary Use | Editing, analyzing text | Generating content |
| Strength | Context understanding | Natural text generation |
| Limitations | Cannot create long-form text | May produce inaccurate facts |
Together, BERT and GPT can streamline workflows, combining precise analysis with fluid writing.
BERT vs GPT: Key Differences for Writing Tasks
GPT vs BERT Explained : Transformer Variations & Use Cases Simplified
How BERT Works for Writing Tasks
BERT processes entire sentences simultaneously, capturing the full context to identify subtle errors. This comprehensive approach allows BERT to understand meaning more precisely and catch mistakes that simpler, unidirectional models might overlook.
Bidirectional Context Analysis
Take the word "bank", for example. When BERT encounters it, the model doesn't just look at the word itself - it examines the entire sentence to figure out its meaning. If the sentence includes terms like "debit card", BERT interprets "bank" in a financial sense. But if it spots words like "river", the model understands that the word refers to a geographical feature.
This precision comes from BERT's transformer-based attention mechanism, which maps relationships between all words in a sentence, no matter how far apart they are. BERT was trained using Masked Language Modeling (MLM), a method where random words are hidden, and the model predicts them based on the surrounding context. This training, applied to a massive dataset of 3.3 billion words from sources like English Wikipedia and Google's BooksCorpus, sharpened BERT's ability to identify incorrect or missing words.
BERT also excels at resolving pronoun references, a skill known as coreference resolution. For example, it can accurately determine when "he", "him", and "his" refer to the same person in a passage. Its Next Sentence Prediction (NSP) training further enhances its ability to ensure coherence across sentences. Together, these capabilities make BERT highly effective in tasks requiring deep contextual understanding.
Editing and Text Analysis Applications
BERT's strong grasp of context makes it a standout tool for analytical editing. In Grammatical Error Detection (GED), for instance, BERT-Base and BERT-Large consistently outperform other systems like ELMo and Flair when tested on datasets such as CoNLL-2014 and JFLEG. It can spot grammar mistakes, awkward phrasing, and stylistic inconsistencies with impressive accuracy.
But BERT's abilities go beyond grammar. It’s equally adept at sentiment analysis, tone control, and Named Entity Recognition (NER). Whether it's identifying subtle shifts in tone or pinpointing names, locations, or organizations within text, BERT ensures logical and consistent flow - an essential feature when editing longer documents.
Understanding how BERT processes and analyzes text provides a solid foundation to compare its performance with GPT's text generation capabilities in the upcoming sections.
How GPT Works for Writing Tasks
GPT takes a unique approach to writing by predicting what comes next in a sequence, rather than analyzing existing text like BERT does. Using a decoder-based architecture, GPT processes text from left to right, mimicking how humans naturally write. This sequential approach makes it particularly effective at generating content that flows smoothly and logically. While BERT focuses on analyzing and understanding, GPT emphasizes creating and expanding ideas.
The model uses an attention mechanism to map relationships between words, which helps it maintain context even across lengthy passages. With training on an extensive 45TB dataset of text, GPT has a vast knowledge base to draw from. One of its standout features is Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), which enables it to follow detailed instructions, adopt a conversational tone, and acknowledge when it lacks information. OpenAI explains its functionality succinctly:
"GPT-4 is a Transformer-based model pre-trained to predict the next token in a document."
Natural Text Generation
GPT can seamlessly continue your prompts, whether you're drafting emails, brainstorming ideas, or writing blog posts. Its ability to generate text naturally and flexibly makes it highly versatile. Thanks to few-shot learning, the model can handle new writing tasks with just a few examples - or even a simple description. This adaptability allows GPT to excel in both creative and structured writing, maintaining a logical flow throughout.
Creative and Long-Form Writing Applications
Because GPT processes text sequentially, it’s particularly suited for creative projects like poetry, scripts, or marketing copy - all while preserving narrative consistency. Its ability to reason through complex topics and apply common sense makes it effective for storytelling and extended content creation. For larger projects, GPT-4o offers a 128,000-token context window, enabling it to handle entire chapters without losing track of earlier details. This feature is invaluable for writing blog posts, reports, or other long-form pieces where consistency is critical.
The model can adapt to various writing styles by analyzing sample texts to identify patterns in tone, sentence structure, and pacing. Whether you need a formal report, a casual blog post, or an authoritative guide, GPT adjusts based on your input. However, since GPT generates content rather than verifying it, it can occasionally produce information that sounds convincing but is inaccurate. Pairing it with fact-checking or retrieval tools ensures greater reliability in professional contexts.
sbb-itb-df9dc23
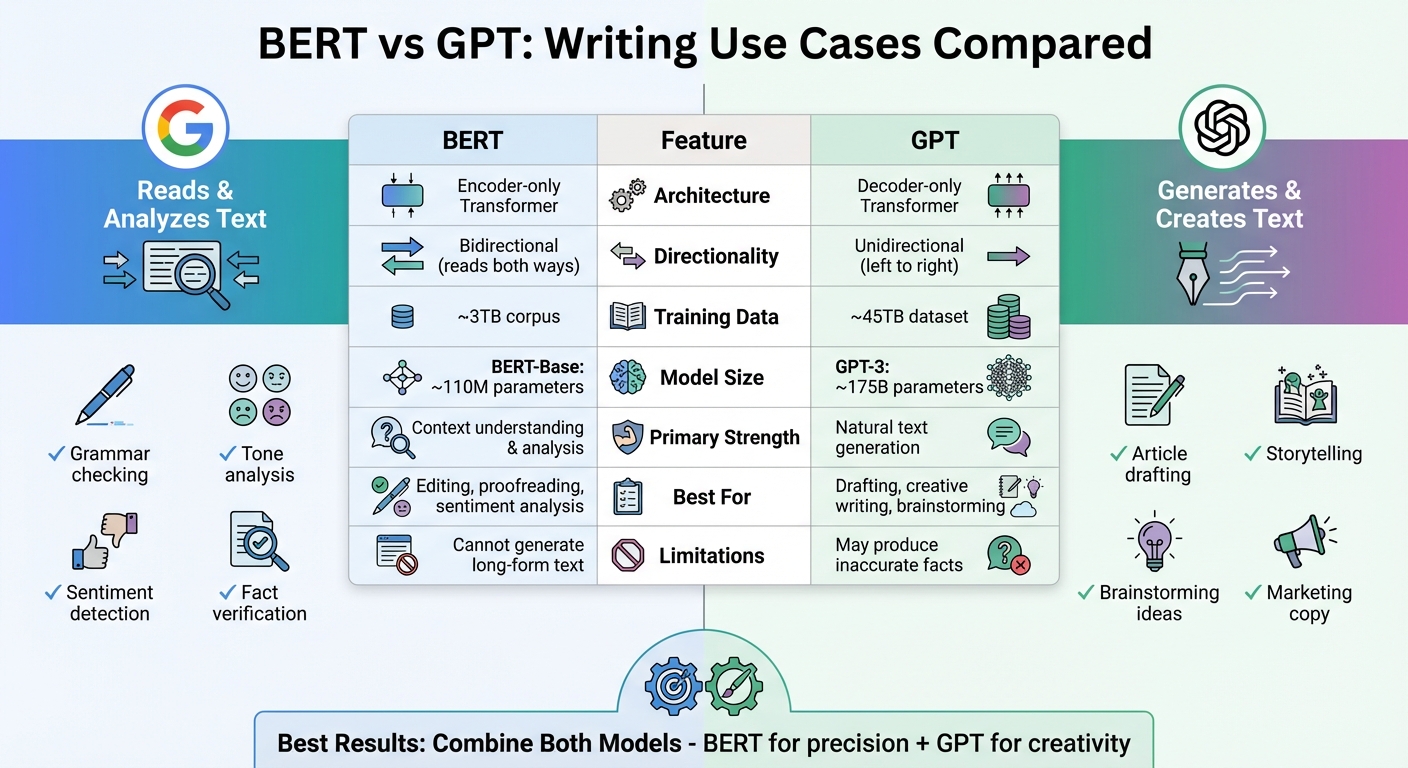
BERT vs GPT: Direct Comparison for Writing
BERT and GPT may both belong to the Transformer family, but they serve very different purposes. Think of BERT as the model that refines and GPT as the one that creates. BERT processes text bidirectionally, meaning it looks at both the left and right context to understand meaning. On the other hand, GPT processes text unidirectionally, moving left to right, which makes it ideal for generating content like sentences and paragraphs. These core differences shape how each model is applied in writing tasks.
Comparison Table: BERT vs GPT
| Feature | BERT | GPT |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture Type | Encoder-only Transformer | Decoder-only Transformer |
| Directionality | Bidirectional (left and right context) | Unidirectional (left-to-right context) |
| Training Objective | Masked Language Modeling (MLM) | Autoregressive next-token prediction |
| Primary Strength | Text comprehension and extraction | Natural text generation and synthesis |
| Writing Use Case | Editing, proofreading, sentiment analysis | Drafting, creative writing, brainstorming |
| Typical Output | Classifications, labels, or embeddings | Sentences, paragraphs |
| Model Size | BERT-Base: ~110M parameters | GPT-3: ~175B parameters |
| Training Data | ~3TB corpus | ~45TB dataset |
| Limitations | Cannot generate long-form creative text | Can produce "hallucinations" or inaccurate facts |
This table highlights how each model's architecture and capabilities align with specific writing needs.
When to Use BERT vs GPT for Writing
BERT shines when precision and analysis are key. It’s perfect for tasks like spotting tone changes, correcting grammar, verifying facts, or pulling out important details from research papers. With its smaller size - around 110 million parameters - it’s efficient enough to run on typical hardware, making it ideal for real-time editing or sentiment analysis tasks.
GPT, on the other hand, is your go-to for generating content. Whether you need to draft an article, write a story, or brainstorm creative ideas, GPT’s massive scale (175 billion parameters in GPT-3) makes it a powerhouse for content creation. Its popularity is reflected in the rapid adoption of ChatGPT, which became the fastest app to hit 100 million users within two months of its launch in February 2023.
For the best results, combine the two. Use BERT to analyze and extract structured information, such as key facts or sentiment, and then let GPT transform that data into polished, engaging content. This hybrid method gives you the best of both worlds: BERT’s analytical precision paired with GPT’s natural writing flow. Together, they can produce content that’s both accurate and engaging.
How Revise Uses BERT and GPT
Revise combines the analytical precision of BERT with the creative capabilities of GPT to tackle a range of writing tasks, from quick edits to crafting long-form content. This pairing ensures that the platform serves both technical accuracy and creative expression.
BERT for Precision Editing
BERT's bidirectional design is key to Revise's ability to fine-tune text. It powers features like custom style adjustments and tone refinement, ensuring your writing aligns with your intent. By analyzing text in both directions, BERT identifies inconsistencies and adjusts tone seamlessly. It also excels at handling words with multiple meanings by generating specific contextual vectors - enhancing clarity and precision.
For example, BERT's nuanced understanding improves Revise's Smart Compose feature, predicting text that complements your writing style and intent. This makes it an ideal tool for tasks requiring meticulous attention to detail.
GPT for Content Creation
When it comes to drafting and brainstorming, Revise leverages advanced GPT models (like GPT-4 and GPT-5, available in Pro and Ultra plans). These models transform rough ideas into polished content, supporting over 170,000 writers and teams in creating everything from books to blog posts and marketing materials.
Revise offers two distinct modes for different needs:
- Speed Mode: Powered by GPT-3.5, this option is perfect for quick tasks where time is a priority.
- Power Mode: Using GPT-4/5, this mode focuses on quality, excelling at complex prompts and delivering highly refined output.
As Stew Fortier, Co-Founder & CEO of Type, notes:
"GPT-4 performs better across a range of writing tasks. It also generates more accurate and factual information. It's slow, though! But when quality is more important than speed, GPT-4 shines."
In Power Mode, GPT-4/5 handles intricate prompts, such as mimicking specific character voices or incorporating dialects and slang to match your style. The integration also supports multimodal inputs, allowing users to turn handwritten notes or sketches into drafts. With a context window of 128,000 tokens (equivalent to roughly 300 pages), Revise can process large documents in one go. Pro plans include up to 200,000 words per month, while Ultra plans extend this to 2,000,000 words - ideal for high-volume writing needs.
Combining BERT and GPT for Better Results
Revise employs a hybrid system where BERT acts as the encoder, refining your input, while GPT serves as the decoder, generating fluid and creative text. BERT tackles issues like tone inconsistencies and grammatical errors with precision, while GPT adds flexibility and creativity to the final output. To address GPT's occasional inaccuracies, Revise incorporates BERT-powered validation layers to fact-check content.
This collaboration ensures that your writing is both accurate and engaging, offering a tailored solution for tasks that demand precision, creativity, or both. The hybrid approach allows Revise to adapt to your specific writing goals, whether you're working on a quick draft or a detailed, high-quality project.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Writing
Key Differences Between BERT and GPT
In simple terms, BERT reads, and GPT writes. BERT's bidirectional design allows it to excel at editing tasks, such as refining tone or performing sentiment analysis with precision. On the other hand, GPT thrives in creative content generation, whether it's drafting, brainstorming, or storytelling.
Looking at the numbers, GPT-4 was trained on a massive 45 TB of data with 1.5 billion parameters, while BERT was trained on 3 TB with 340 million parameters. This gives GPT a broader creative scope, while BERT's more focused design ensures accuracy for analytical tasks. These complementary strengths are the backbone of Revise's strategy, combining precise editing with dynamic creation.
Getting Started with AI Models in Revise
Revise takes advantage of these differences by integrating both models to streamline your writing process. BERT analyzes your style and intent, ensuring the tone and structure are just right. Meanwhile, GPT-based models generate content that aligns with your voice. Whether you're polishing an email or drafting a full manuscript, Revise adapts to your specific needs.
For those ready to dive in, Revise offers two subscription plans:
- Pro Plan: $8 per month (or $96 annually). Includes up to 200,000 words monthly and access to premium models like GPT 5.1 and Gemini 2.5 Flash.
- Ultra Plan: $20 per month (or $240 annually). Supports up to 2,000,000 words monthly and features advanced models like Claude Sonnet 4.5, along with extra functionalities and priority support.
These plans ensure flexibility, whether you're a casual writer or need high-volume, advanced tools.
FAQs
How do BERT and GPT work together in writing tasks?
BERT and GPT work hand-in-hand by leveraging their distinct strengths in writing tasks. BERT shines when it comes to understanding and analyzing text. It's perfect for tasks like sentiment analysis, text classification, or answering questions where deep comprehension is key.
Meanwhile, GPT is all about generating fluent, human-like text. Whether it's crafting engaging content, generating dialogues, or completing a piece of text, GPT excels at producing creative and coherent output.
Together, they form a powerful duo. BERT takes on the heavy lifting of context analysis and understanding, while GPT handles the creative aspects of text generation. This combination makes AI systems more versatile, blending comprehension with creativity for improved writing tasks.
What challenges come with using GPT for content creation?
GPT models have a knack for producing content that sounds polished, but it’s not always accurate. Why? These models are trained on massive internet datasets, and unfortunately, that includes errors, outdated details, and misinformation. This means they can sometimes stumble, especially when tackling very specific or complex topics.
Another challenge is consistency. GPT can generate repetitive or inconsistent responses, which might affect the quality of the content. And when it comes to understanding subtle context or diving deep into specialized fields, it can fall short unless it's been fine-tuned with targeted data. For tasks that demand accuracy or expert-level insight, a thorough review and careful editing of GPT-generated content are absolutely necessary.
When is BERT a better choice than GPT for editing tasks?
BERT stands out when it comes to editing tasks that demand a strong grasp of context and the intricate relationships within text. It's particularly effective for activities like text classification, question answering, and identifying subtle language nuances. This makes it a solid choice for enhancing clarity and ensuring precision in writing.
On the other hand, if your goal is to produce creative, human-like content or develop longer pieces, GPT might be the better fit. But for tasks where comprehension and contextual accuracy are key, BERT remains the preferred tool.