How AI Handles Punctuation in Voice Transcription

AI transcription systems don't just convert speech into text - they also decide where punctuation goes. This involves analyzing grammar, speech patterns, and acoustic cues like pauses and intonation. Accurate punctuation is critical for readability and meaning, as seen in examples like "Let's eat, grandma!" versus "Let's eat grandma!" Modern tools use advanced neural networks and real-time processing to place commas, periods, and question marks effectively. However, challenges like background noise, accents, and filler words can still impact accuracy. Recent advancements, such as models trained on diverse datasets and speaker-adaptive AI, have improved performance, making these systems more reliable for tasks like journalism, law, and sentiment analysis.
Key points:
- AI uses transformer models to understand context and place punctuation.
- Prosodic factors (intonation, pauses) and grammar guide decisions.
- Preprocessing and post-processing refine punctuation and formatting.
- Challenges include noise, accents, and natural speech variations.
- New models like "Cadence" handle spontaneous speech and multiple languages.
Quick Tip: Test transcription tools under conditions similar to your real-world use to ensure the best results.
How to Use OpenAI's Whisper for Perfect Transcriptions (Speech to Text)
How AI Adds Punctuation to Voice Transcripts
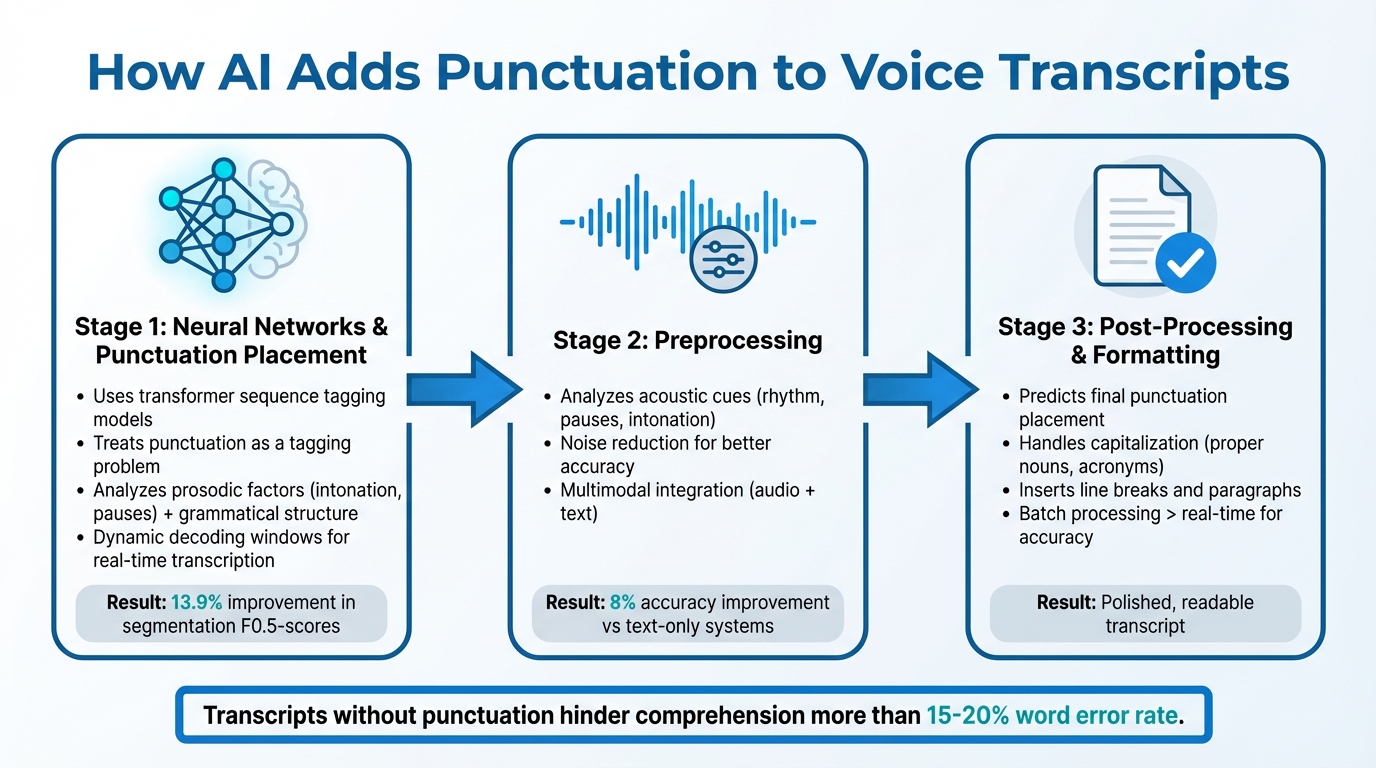
How AI Adds Punctuation to Voice Transcripts: 3-Step Process
AI punctuation follows a three-step process that transforms spoken words into clear, readable text. Each phase plays a crucial role, from understanding context to refining the final transcript.
Neural Networks and Punctuation Placement
Modern AI uses advanced transformer sequence tagging models to determine where punctuation should go. These models analyze the words before and after a specific point, capturing a wide range of context in both directions.
"Transformer sequence tagging models are effective at capturing long bi-directional context, which is crucial for automatic punctuation", says Microsoft Corporation.
The process treats punctuation as a tagging problem, assigning labels like "comma", "period", or "question mark" to spaces between words. This relies on both prosodic factors - intonation and pauses - and grammatical structure, using statistical models to make decisions. This dual approach performs better than older systems that focused only on pauses, which often misinterpreted hesitations or run-on sentences.
Real-time transcription adds complexity since future context isn't available. To handle this, AI uses dynamic decoding windows to make punctuation decisions on the fly. Research from Microsoft shows that a streaming approach improved segmentation F0.5-scores by 13.9% in continuous speech scenarios. These initial punctuation placements are then fine-tuned in the preprocessing stage.
How Preprocessing Improves Punctuation Accuracy
Preprocessing enhances accuracy by refining the data with acoustic cues. AI systems analyze raw audio for patterns like rhythm, pauses, and intonation - prosodic signals that naturally indicate sentence breaks. However, background noise or poor audio quality can interfere with this process, making noise reduction a critical first step.
The most effective systems also use multimodal integration, combining audio data with text. Studies reveal that models trained on both audio and text improve punctuation accuracy by 8% compared to text-only systems.
Post-Processing and Transcript Formatting
Once neural analysis and preprocessing are complete, post-processing ensures the transcript is polished and easy to read. Specialized models predict where punctuation like commas, periods, and question marks should go.
"Automatic punctuation transforms raw speech transcription into readable, structured text that powers modern Voice AI applications", explains Kelsey Foster from AssemblyAI.
This phase also handles capitalization, applying it to proper nouns, organizations, and acronyms like NASA - details often overlooked earlier in the process. To further enhance readability, the system inserts line breaks and paragraphs, avoiding the appearance of one massive block of text. Research highlights that transcripts without punctuation hinder comprehension more than a word error rate of 15%-20%.
Batch processing outshines real-time transcription in accuracy because it allows the AI to analyze the entire recording before deciding where punctuation belongs. With full context, the system can better distinguish between true sentence endings and simple pauses, delivering a cleaner, more accurate transcript.
Common Problems with AI Punctuation Detection
Even the most advanced AI systems face hurdles when it comes to punctuating voice transcripts. The core issue lies in the difference between how people speak and how text is typically written. This mismatch creates challenges that technology is still working to address. Below, we’ll dive into the main factors affecting punctuation accuracy and how newer AI models are tackling these problems.
What Affects Punctuation Accuracy
One major issue is background noise, which can account for up to 45% of transcription errors. Noise makes it harder for AI to pick up on key audio cues like pauses or intonation changes - both of which are critical for placing punctuation correctly.
Accents and dialects add another layer of difficulty. Most systems are trained on standard American English, so when they encounter regional accents or non-native pronunciations, error rates can jump to 16%–28%. By comparison, for native speakers, error rates hover between 6%–12%.
Speech speed also plays a role. Rapid speech can blur word boundaries, while very slow or uneven pacing can lead to over-segmentation, making it tough for AI to detect where sentences begin or end. On top of that, filler words like "um", "uh", or "like" disrupt the grammatical flow, often leading to misplaced punctuation.
Another challenge is the natural flow of human speech, which doesn’t always follow the rules of written grammar. People pause mid-sentence or ramble into run-on sentences, which can confuse AI systems and result in misplaced or missing punctuation.
"Punctuation plays a vital role in structuring meaning, yet current models often struggle to restore it accurately in transcripts of spontaneous speech, especially in the presence of disfluencies such as false starts and backtracking."
– Sidharth Pulipaka, Ashwin Sankar, and Raj Dabre
These difficulties highlight why improvements in AI models are so important, as outlined in the next section.
How Adaptive AI Improves Punctuation
To address these challenges, modern AI systems rely on massive datasets of transcribed audio. For instance, platforms like Rev use transcripts from over 60,000 human transcriptionists to train their models. This exposure to diverse speech patterns helps the AI learn how natural speech flows and improves its ability to handle variations.
A significant breakthrough came in December 2025, when researchers Sidharth Pulipaka, Ashwin Sankar, and Raj Dabre unveiled "Cadence." This punctuation restoration model, built on a pretrained Large Language Model, was specifically designed to handle spontaneous speech. It also expanded support to 22 Indian languages in addition to English, outperforming earlier models. This development signals a step forward in creating AI systems that can adapt to different languages and speaking styles.
Another advancement is speaker-adaptive AI, which fine-tunes itself to individual speech patterns, including accents and rhythms, to improve accuracy. On top of that, systems that incorporate user feedback have shown impressive results, with Word Error Rates dropping by 6%–10% and speaker identification accuracy improving by 8%. This continuous learning process means the AI gets better at understanding and punctuating your unique way of speaking over time.
sbb-itb-df9dc23
AI Model Performance Comparison for Punctuation
When evaluating AI transcription systems, understanding how they handle punctuation is crucial. Performance can vary widely depending on the audio quality and the type of speech being transcribed. The following comparisons highlight how different models tackle these challenges in real-world conditions.
OpenAI Whisper stands out for its ability to handle diverse scenarios effectively. Trained on an impressive 680,000 hours of audio - 33% of which is non-English - it performs exceptionally well in noisy environments and with unfamiliar accents. In tests across various datasets, Whisper made 50% fewer errors than models built specifically for benchmark tests like LibriSpeech, showcasing its adaptability in challenging audio conditions.
On the other hand, AssemblyAI's Universal Model comes with punctuation, casing, and Inverse Text Normalization (ITN) enabled by default. This model excels at identifying proper nouns and producing transcripts with natural structure, making it an excellent choice for customer-facing applications.
Meanwhile, Google Cloud Speech-to-Text offers extensive customization options but requires users to manually activate punctuation. It supports periods, commas, and question marks, along with auto-capitalization after periods. Google also provides $300 in free credits for new users to explore the system's capabilities.
AI Model Comparison Table
| Model | Punctuation Marks | Default Settings | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAI Whisper | Periods, commas, question marks, etc. | Enabled | Noisy environments, accents, multilingual audio |
| AssemblyAI Universal | Periods, commas, question marks, exclamation marks | Punctuation + ITN enabled | Noun recognition, structured transcripts |
| Google Cloud STT | Periods, commas, question marks | Disabled (manual enable required) | Highly customizable language configurations |
These comparisons emphasize the importance of testing models in conditions that reflect your actual use case. For instance, while leading AI systems achieve near-human punctuation accuracy in controlled settings, their real-world performance can differ significantly. Research with Cadence illustrates this point: its performance dropped from a Macro F1 score of 0.76 on formal text to 0.60 on spontaneous speech. On the IndicCorp-v2 dataset, Cadence outperformed competitors like IndicPunct and DeepMultilingualPunctuation, which both scored 0.54. However, on the more challenging IndicVoices dataset of spontaneous speech, Cadence's score fell to 0.60, while IndicPunct remained at 0.54.
This variation underscores why testing with audio that mirrors your real-world scenarios is so important. A model that excels with clean, scripted audio may struggle with spontaneous, conversational speech. While many AI models today rival human editors in punctuation accuracy for general-purpose audio, it’s worth noting that streaming transcription tends to be less accurate than batch processing, as the AI has less context to draw from.
How Revise Handles Voice-to-Text Punctuation
Revise takes advantage of advanced neural networks to handle punctuation in voice transcriptions with precision. Using transformer neural networks - an advanced form of deep learning - the platform automatically inserts punctuation marks as you speak. This means you can focus on expressing your thoughts naturally without worrying about manually adding commas, periods, or question marks later. By applying proven AI techniques, Revise ensures your spoken words transition effortlessly into well-structured written text.
Speech-to-Text Punctuation Tools
Revise's system combines acoustic and grammatical cues to determine the correct placement of punctuation. It analyzes elements like tone and sentence structure to ensure accuracy. Trained on a rich dataset curated from professional transcriptionists, the AI models are equipped to handle the nuances of converting spoken language into text. One standout feature is its use of Inverse Text Normalization (ITN), which transforms phrases like "June twentieth" into "June 20th." Together, these features deliver clear, polished transcripts.
You can also customize the tool to fit your specific workflow. Whether you're drafting an email, working on a lengthy article, or jotting down quick ideas, Revise adapts to your writing style while maintaining consistent punctuation accuracy. This flexibility is available on both the Pro and Ultra plans, catering to different user needs.
Time-Saving Benefits for Writers
Revise removes the hassle of manually adding punctuation, saving you valuable time. Instead of reviewing transcripts for formatting, you can focus on refining your ideas and improving your content. Over time, as the system learns your preferences, it aligns its punctuation choices with your unique writing style. This makes the process of turning spoken thoughts into polished text quicker and more seamless.
Conclusion
AI has transformed how voice transcription systems handle punctuation, turning spoken words into well-structured text with minimal human intervention. Modern tools rely on transformer neural networks and bidirectional attention mechanisms to understand context, delivering near-human levels of accuracy. These advancements tackle challenges like semantic ambiguity and improve downstream tasks such as sentiment analysis and entity recognition, where accurate punctuation plays a crucial role.
The evolution from rule-based approaches to deep learning has shown clear progress. For instance, AssemblyAI's 2023 model update, trained on a dataset of 13 billion words, achieved an 11% boost in overall punctuation accuracy and a 39% improvement in F1 scores for mixed-case words. Additionally, human evaluators preferred the updated neural punctuation models 61% of the time compared to earlier versions. These improvements are now integral to platforms designed to boost productivity for writers and professionals alike.
Building on these advancements, Revise incorporates sophisticated punctuation models to simplify your writing workflow. By combining acoustic analysis with grammatical rules, it eliminates the need for manual transcript editing. Features like Inverse Text Normalization ensure that dates, numbers, and other elements are consistently formatted.
For content creators who deal with large volumes of material, this automation reduces time spent on tedious reviews, allowing more energy to focus on creativity and refinement. As the system adapts to your writing style over time, it becomes more attuned to your preferences, making the process even smoother.
FAQs
How does AI manage punctuation in challenging audio environments?
AI approaches punctuation in tricky audio settings by using sophisticated algorithms designed to interpret speech patterns and context. Techniques such as dynamic decoding windows and bidirectional context analysis help these systems predict punctuation accurately, even when dealing with uneven pauses or fluctuating speech speeds.
By adjusting in real-time to the audio input, AI ensures transcriptions stay clear and organized, even when background noise or speaker differences come into play.
How does AI use speech patterns to add punctuation in transcriptions?
AI uses prosodic factors - like intonation, stress, rhythm, and pauses - to figure out where punctuation should go in voice-to-text transcriptions. These speech patterns act as signals, helping the AI detect sentence boundaries and organize text, which is especially useful in conversational or spontaneous speech where punctuation isn’t explicitly provided.
By studying these prosodic elements, advanced AI systems can produce more accurate and readable transcriptions. For example, they can handle irregular pauses or disfluencies in natural speech, making the final text flow more smoothly and align better with the speaker's intended meaning.
How do AI models enhance punctuation accuracy in voice-to-text for different languages?
AI models have made strides in improving punctuation accuracy for voice-to-text transcription by using advanced multilingual language models. These models are trained on a variety of datasets, enabling them to understand language-specific punctuation rules and adapt to the differences between spoken and written language - even in challenging environments like those with background noise or limited resources.
Key techniques such as domain-specific fine-tuning, data augmentation, and multimodal embeddings play a crucial role in refining these systems. They help AI better understand accents, speech patterns, and subtle linguistic differences. As a result, these models can restore punctuation more effectively across different languages and scenarios, leading to transcriptions that feel more polished and natural.